Pulmonary rehabilitation is a supervised program combining exercise and education to improve lung health, reduce symptoms, and enhance overall well-being for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions.
1.1 Definition and Purpose
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a structured, supervised program combining exercise and education to enhance lung function, reduce symptoms, and improve quality of life for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions. Its purpose is to optimize physical fitness, manage breathlessness, and empower patients with strategies to maintain long-term health and independence.
1.2 Overview of Benefits
Pulmonary rehabilitation offers numerous benefits, including improved exercise capacity, enhanced quality of life, and better symptom management. It increases energy levels, reduces breathlessness, and empowers individuals to manage their condition effectively. Regular participation also fosters psychological well-being and long-term independence, making it a cornerstone of chronic respiratory care.
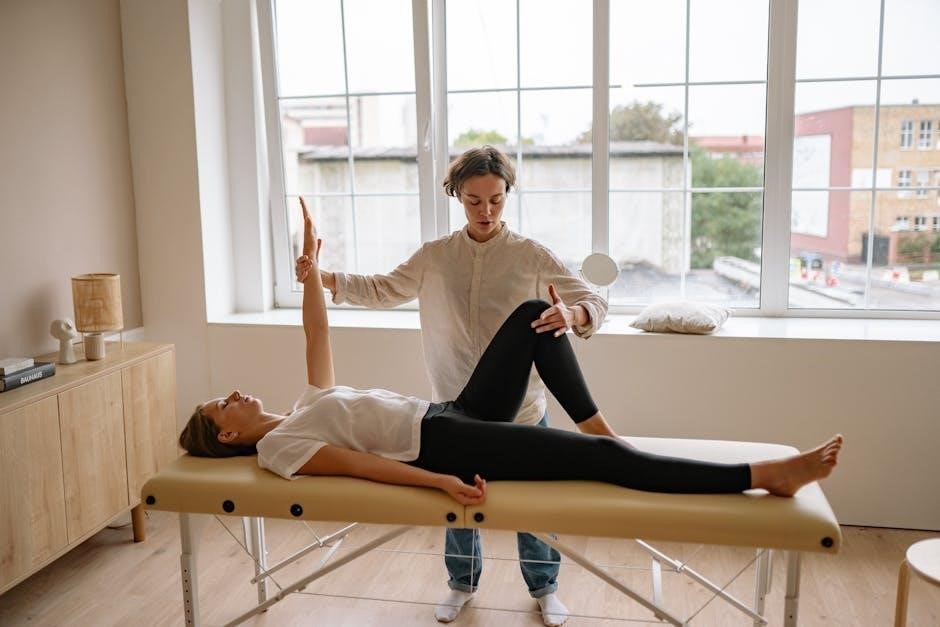

Key Components of Pulmonary Rehabilitation Programs
Pulmonary rehabilitation integrates exercise training, breathing techniques, and education to manage symptoms, enhance physical function, and improve overall health for individuals with chronic lung conditions.
2.1 Exercise Training
Exercise training is a cornerstone of pulmonary rehabilitation, focusing on endurance, strength, and flexibility. It includes aerobic exercises like walking or cycling, resistance training, and stretching. These activities aim to improve muscle function, increase oxygen efficiency, and enhance overall physical capacity. Supervised sessions often incorporate warm-up routines and cool-down stretches to ensure safety and effectiveness, tailored to individual patient needs and progress.
2.2 Breathing Techniques
Breathing techniques are essential in pulmonary rehabilitation, focusing on improving lung function and reducing breathlessness. Methods like pursed lip and belly breathing help manage shortness of breath, enhance oxygen exchange, and promote relaxation. These exercises are tailored to individual needs, often practiced alongside physical activity to optimize respiratory efficiency and overall comfort during daily tasks and exercise routines.
2.3 Education on Lung Disease Management
Education on lung disease management empowers patients to understand their condition, manage symptoms, and adhere to treatment plans. Topics include lung function, medication use, and lifestyle adjustments. This component of pulmonary rehabilitation helps patients make informed decisions, reducing complications and improving long-term health outcomes.
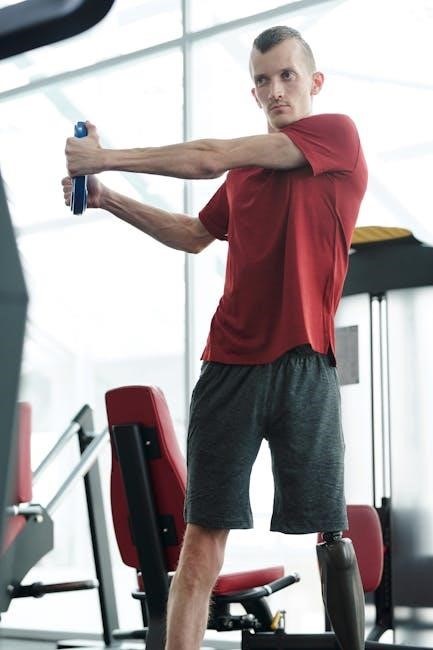

Breathing Exercises in Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Breathing exercises are core to pulmonary rehabilitation, enhancing lung function and reducing breathlessness. Techniques like pursed lip and belly breathing improve respiratory efficiency and overall well-being effectively.
3.1 Pursed Lip Breathing
Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) is a simple yet effective technique taught in pulmonary rehabilitation. It involves exhaling slowly through pursed lips, as if blowing out a candle, to slow breathing and keep airways open longer. This method improves lung function, reduces shortness of breath, and enhances oxygen exchange. Regular practice of PLB can significantly improve breathing patterns and overall comfort in daily activities, making it a cornerstone of pulmonary rehabilitation programs.
3.2 Belly Breathing (Diaphragmatic Breathing)
Belly Breathing, or diaphragmatic breathing, engages the diaphragm to maximize lung expansion. It involves inhaling deeply through the nose, allowing the belly to rise, and exhaling slowly through pursed lips. This technique enhances lung capacity, reduces breathlessness, and improves oxygen exchange. Regular practice strengthens the diaphragm and promotes relaxation, making it a cornerstone of pulmonary rehabilitation for managing chronic respiratory conditions effectively.
Physical Exercises for Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Physical exercises in pulmonary rehabilitation include endurance, strength, and flexibility training to improve muscle function and cardiovascular health, enhancing overall physical capacity and lung health.
4.1 Endurance Training
Endurance training focuses on improving cardiovascular health and increasing stamina through activities like walking, cycling, or swimming. These exercises enhance muscle function and boost energy levels, helping patients with chronic lung conditions to perform daily tasks with greater ease and manage breathlessness more effectively. Regular endurance exercises are tailored to individual fitness levels to ensure safety and gradual progress.
4.2 Strength Training
Strength training involves exercises targeting specific muscle groups to build power and endurance. Using weights or resistance, patients enhance muscle function, improving mobility and daily activity performance. This training is tailored to individual capabilities, focusing on upper and lower body strength, which helps stabilize posture and reduce fatigue, ultimately supporting better overall lung health and functional independence. Regular practice ensures consistent progress and improved quality of life.
The Role of Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Managing COPD
Pulmonary rehabilitation helps COPD patients improve exercise tolerance and quality of life through structured exercise and education, managing symptoms and slowing disease progression effectively.
5.1 Improving Exercise Tolerance
Pulmonary rehabilitation enhances exercise tolerance in COPD patients through tailored endurance and strength training. Supervised programs include walking or resistance exercises to boost stamina and muscle strength. Techniques like the Borg scale help monitor effort, ensuring safe progression. Gradually increasing exertion levels helps patients achieve greater physical endurance, reducing breathlessness during daily activities and improving functionality and independence.
5.2 Enhancing Quality of Life
Pulmonary rehabilitation significantly improves quality of life by reducing symptoms like breathlessness and fatigue. Patients gain confidence and independence, enabling them to perform daily tasks with greater ease. The program also addresses emotional well-being, reducing anxiety and depression. Education on disease management empowers individuals to take control of their health, fostering a positive outlook and improving overall satisfaction with life.
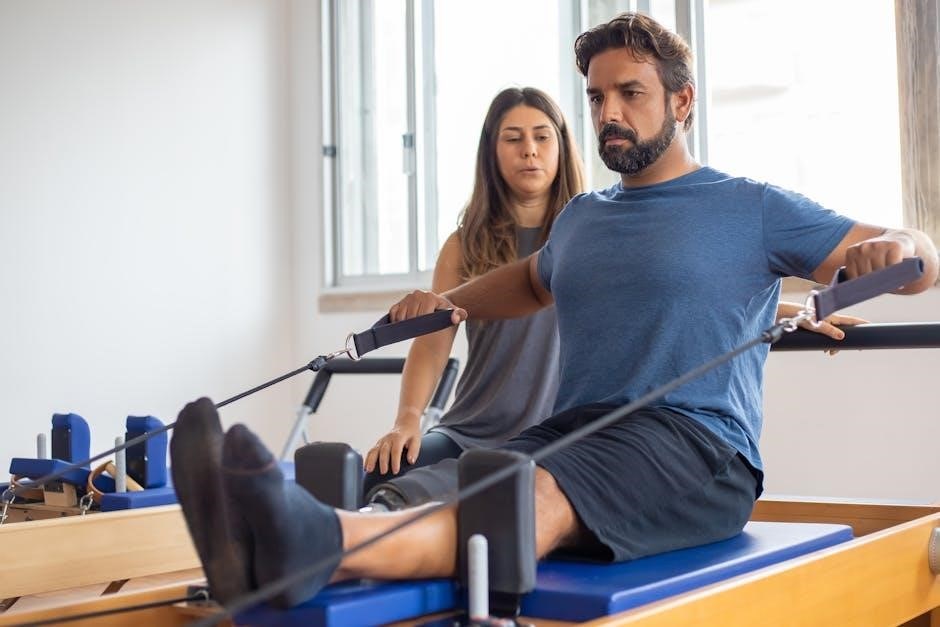

Monitoring Progress and Safety
Monitoring progress and safety in pulmonary rehabilitation involves regular assessments using tools like the Borg Scale to measure effort and adjust exercise intensity, ensuring a safe and effective program.
6.1 Using the Borg Scale for Effort
The Borg Scale is a tool used to measure perceived exertion during exercise in pulmonary rehabilitation. Patients rate their breathlessness and fatigue on a scale from 0 to 10, helping clinicians adjust exercise intensity safely. This ensures activities remain challenging yet manageable, promoting progress without overexertion. Regular use of the Borg Scale enhances individualized programming and improves exercise tolerance over time.
6.2 Adjusting Exercise Intensity
Exercise intensity in pulmonary rehabilitation is tailored to individual tolerance, ensuring safety and effectiveness. Adjustments are based on symptoms, oxygen levels, and patient feedback. Gradual progression helps improve endurance without overexertion. Clinicians monitor progress and modify routines to optimize benefits, ensuring exercises remain challenging yet manageable. This personalized approach enhances physical capacity and overall well-being for patients with chronic respiratory conditions.
Home Exercise Programs
Home exercise programs are essential for continuing pulmonary rehabilitation, helping maintain lung health and manage symptoms through regular routines and breathing techniques.
7.1 Creating a Personalized Plan
Creating a personalized home exercise plan involves tailoring routines to individual needs, ensuring safety and effectiveness. It includes specific exercises, goal setting, and progress monitoring using tools like the Borg Scale. The plan should incorporate endurance and strength training, along with breathing techniques, to improve lung function and overall fitness. Regular adjustments ensure continued progress and adaptability to changing health conditions.
7.2 Adherence and Long-Term Benefits
Consistent adherence to home exercise programs enhances physical fitness, reduces symptoms, and improves quality of life. Regular participation in pulmonary rehabilitation exercises leads to long-term health benefits, including better lung function, increased energy levels, and reduced hospital admissions. Motivation and support systems play a crucial role in maintaining adherence and maximizing the positive outcomes of the program.

The Importance of Education in Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Education empowers patients to manage lung disease effectively, understand symptoms, and use medications properly, leading to better adherence and improved long-term health outcomes.
8.1 Understanding Lung Function
Understanding lung function is crucial in pulmonary rehabilitation, as it helps patients grasp how their lungs work and the impact of diseases like COPD. Education focuses on the mechanics of breathing, the role of the diaphragm, and how air flows in and out of the lungs. This knowledge enables patients to better manage symptoms and adhere to treatment plans, improving overall respiratory health and quality of life.
8.2 Managing Symptoms and Medications
Effective symptom and medication management is vital for optimizing quality of life in pulmonary rehabilitation. Patients learn to recognize and control symptoms like breathlessness and coughing through tailored techniques. Education on proper medication use, including inhalers and oxygen therapy, ensures safety and efficacy. This empowers individuals to manage their condition confidently, minimizing complications and enhancing long-term health outcomes.

Overcoming Barriers to Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Addressing physical limitations, motivation, and support systems helps overcome barriers to pulmonary rehabilitation, ensuring improved participation and sustained progress for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions.
9.1 Addressing Physical Limitations
Physical limitations, such as reduced mobility or severe breathlessness, can hinder participation in pulmonary rehabilitation. Tailored exercise plans, oxygen therapy, and breathing techniques help manage these challenges. Supervised programs ensure safety, while gradual progression builds tolerance; Incorporating activities like pursed lip breathing and strength training enhances physical capacity, making rehabilitation accessible and effective for individuals with diverse physical abilities and chronic respiratory conditions.
9.2 Motivation and Support Systems
Motivation is crucial for adherence to pulmonary rehabilitation. Support systems, such as family, friends, and group exercise environments, play a significant role in maintaining engagement. Encouragement from healthcare providers and shared experiences with peers foster a sense of community, reducing feelings of isolation. Positive reinforcement and measurable progress further enhance motivation, ensuring long-term commitment to the rehabilitation process and overall well-being.
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a proven, effective intervention enhancing exercise tolerance and quality of life. Future directions include advancing rehabilitation techniques and integrating innovative approaches for better patient outcomes.
10.1 The Impact of Pulmonary Rehabilitation on Patient Outcomes
Pulmonary rehabilitation significantly improves exercise capacity, reduces breathlessness, and enhances quality of life for patients with chronic lung diseases. It also improves physical and emotional well-being, enabling individuals to perform daily activities more effectively. Studies show reduced hospital readmissions and improved long-term health outcomes, making it a vital component in managing chronic respiratory conditions like COPD and pulmonary fibrosis. Regular participation fosters independence and overall health improvement.
10.2 Advances in Rehabilitation Techniques
Recent advancements in pulmonary rehabilitation include telemedicine-based programs, enabling remote access to exercise and education. Wearable technology now monitors progress in real-time, while AI-driven platforms tailor exercises to individual needs. These innovations enhance accessibility, personalization, and engagement, optimizing outcomes for patients with chronic lung conditions. Such advancements ensure pulmonary rehabilitation remains effective and adaptable to diverse patient requirements.